
A component important to life found on one in every of Saturn’s moons, elevating hopes of discovering alien microbes
[ad_1]
Enceladus is the tiny moon of Saturn that appears to have all of it. Its icy floor is intricately carved by ongoing geological processes. Its icy shell overlies an inner, liquid ocean. There, chemically charged heat water seeps out of the rocky core onto the ocean ground—doubtlessly offering nourishment for microbial life.
Now, a brand new examine, revealed in Nature, has uncovered extra proof. It presents the primary proof that Enceladus’s ocean accommodates phosphorus, a component that’s important to life.
The Cassini spacecraft, operated in orbit about Saturn 2004–17 by Nasa and the European House Company (Esa), discovered plumes of ice particles venting from cracks. These penetrate proper by means of the icy shell in order that the ocean water on the backside of every crack is uncovered to the vacuum of house, the place the dearth of confining strain causes it to bubble and vaporize within the type of plumes.
These plumes offered samples of spray from Enceladus’s inner ocean that have been scooped up for evaluation by Cassini throughout a number of shut fly-bys—a bonus that wasn’t anticipated when the mission was initially deliberate.
Particles analyzed throughout these transient passages by means of the plumes demonstrated that the ice is contaminated by traces of easy natural molecules in addition to molecular hydrogen and tiny particles of silica. Taken collectively, these point out that chemical reactions between water and heat rock happen on the ocean ground, likely at “hydrothermal vents” (a fissure releasing heated water) just like these on Earth.
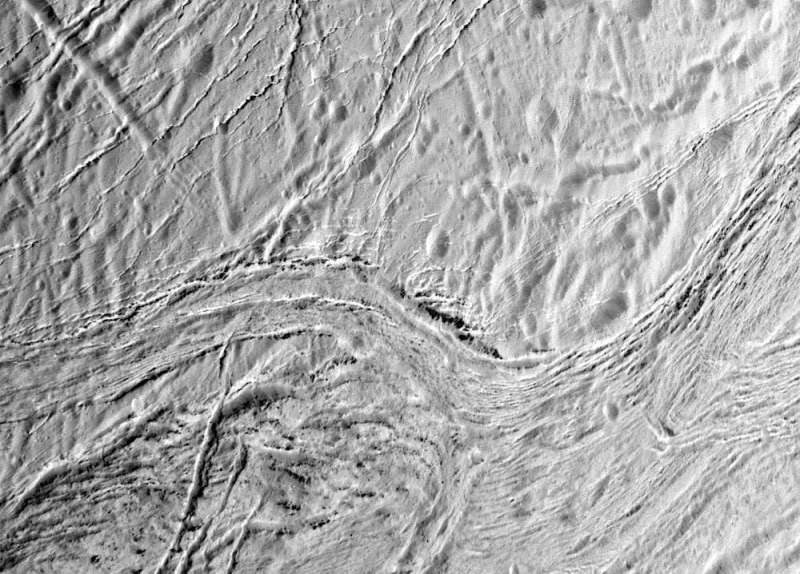

That is vital. It means Enceladus has all of the elements for microbial life to maintain itself (within the absence of daylight). It’s in truth the setting thought of most probably to have helped life on Earth start. If it occurred on Earth it might have occurred inside Enceladus too.
Lacking hyperlink
All life on Earth requires six important components: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur—identified collectively by the scarcely pronounceable acronym CHNOPS. 5 of those six important components have been detected in Enceladus plume samples a number of years in the past, however phosphorus had by no means been discovered.
Phosphorus is a crucial ingredient, as a result of it’s wanted for the phosphate teams (phosphorus plus oxygen) that hyperlink the lengthy chains of nucleic acids comparable to DNA and RNA that retailer genetic data. It additionally permits cells to retailer power via molecules comparable to adenoside triphosphate (ATP for brief).
In fact, we do not know for positive that life inside Enceladus (if it exists) is obliged to make use of nucleic acids or ATP. Nonetheless, as a result of the presence of phosphorus is crucial for all times as we all know it, it makes Enceladus a extra possible prospect now that we’re sure that there’s sufficient phosphorus out there there.

Canny accumulating
The crew discovered Enceladus’s phosphorus by avoiding the cluttered knowledge collected in the course of the Cassini’s frantically fast zooms by means of the plumes. As an alternative, they scoured sparser knowledge accrued in a extra leisurely trend by Cassini’s Cosmic Mud Analyzer throughout 15 intervals between 2004 and 2008 whereas Cassini was touring inside one in every of Saturn’s rings: the “E-ring.” Enceladus travels alongside this hoop because it orbits.
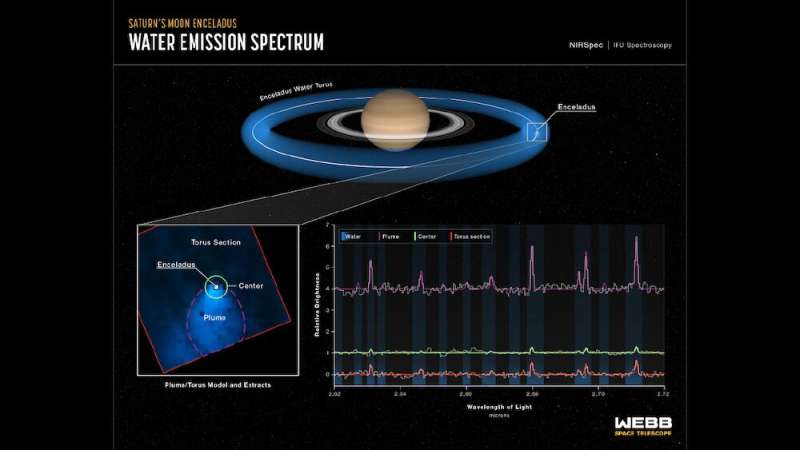
The E-ring hoop is greater than 2,000km thick. About 30% of the ice particles emitted in Enceladus’ plumes find yourself there, as demonstrated by a latest picture from the James Webb House Telescope, which is the one proof we’ve got that the plumes have been nonetheless lively 5 years after the tip of the Cassini mission.
Sorting by means of analyses of almost a thousand ice particles, that are believed to signify frozen spray from Enceladus, the researchers discovered 9 of them that contained phosphates. This may increasingly sound like a slim haul, nevertheless it is sufficient to show that Enceladus has greater than sufficient dissolved phosphorus in its ocean to allow the functioning of life there.
Certainly, follow-up laboratory experiments counsel that the focus of dissolved phosphorus in Enceladus’s ocean water might even be tons of of instances larger than in Earth’s oceans.
The crew argue that their findings and related modeling make it possible that any icy moon that grew farther from the solar than the photo voltaic system’s “carbon dioxide snowline”—a location the place temperatures throughout planetary formation have been low sufficient for carbon dioxide to turn into ice—is more likely to include plentiful phosphorus. This situation is met for icy moons at Saturn and past, however not at Jupiter.
Jupiter’s distance from the solar locations it past the “water-ice snowline” (the place water turns into ice), however it’s too near the solar, and therefore too heat, to be past the carbon dioxide snowline.
So the place does this go away Jupiter’s moon Europa, a goal for missions on account of arrive about ten years from now?
This moon has been extensively touted as doubtlessly in a position to help a extra flourishing biosphere than Enceladus due to its bigger measurement and larger retailer of chemical power in its rocky inside. The crew behind the brand new examine are reticent on this, however their modeling suggests a phosphate focus in Europa’s inner ocean a couple of thousand instances lower than at Enceladus.
To me, that isn’t a gamechanger, and we should always proceed to anticipate Europa to be liveable. However it might be reassuring to seek out some proof of phosphorus there too.
Offered by
The Dialog
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.![]()
Quotation:
A component important to life found on one in every of Saturn’s moons, elevating hopes of discovering alien microbes (2023, June 18)
retrieved 18 June 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-element-essential-life-saturn-moons.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]






