
As anticipated, wine grapes discovered to have excessive deleterious genetic burden
[ad_1]
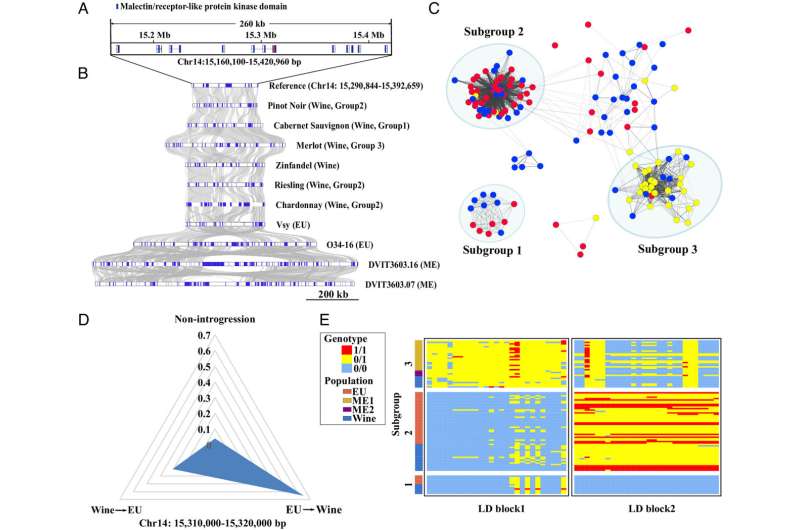
Researchers on the Chinese language Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China, have utilized machine studying to genetic sequence information from wild and home European grapes.
Within the research, “Adaptive and maladaptive introgression in grapevine domestication,” printed in PNAS, the researchers investigated the historical past of genetic hybridization between domesticated grapes and their European wild kinfolk, tracing the origin again to a single domestication occasion in wine grapes.
In response to the research authors, domesticated grapevines unfold to Europe round 3,000 years in the past. Archaeological proof dates the primary domestication of grapevines to round 5,900 BC, with the propagation sylvestris varieties within the South Caucasus, the northern Fertile Crescent, and the Levant.
After their domestication, grapes had been unfold all through the Mediterranean world, diversifying into many regionally tailored varieties. Throughout the final 3,000 years, grapevines had been established in Europe, the place the imported varieties got here into contact with genetically distinct wild sylvestris populations.
Sure gene areas of the wine grapes associated to fragrant compound synthesis had been enriched with wild variations, suggesting that European wild grapes have been an important useful resource for enhancing the flavour of wine grapes.
The group collected present sequencing information from 305 samples and carried out sequencing on 40 samples from the USDA grape germplasm collections in Davis, California utilizing the Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform. The mixed assortment coated a large distributional vary of world wild and cultivated grapes.
Machine studying–based mostly inhabitants genetic evaluation detected proof for a single domestication occasion of a grapevine, adopted by steady gene move between European wild grapes (EU) and cultivated grapes over the previous ~2,000 years.
All through hybridization occasions and intentional breeding enhancements, genetic fragments have been launched with the next deleterious burden, with most deleterious single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and structural variants hidden in a heterozygous state.
The authors recommend that the helpful results of hybridization carry a possible price as sure areas have elevated numbers of recognized deleterious variants. The identification of helpful and deleterious variants might be necessary elements for a extra genomic-based technique of breeding grapevines.
How deleterious?
The suggestion of deleterious burden relies on segments of DNA that aren’t particularly advantageous, normally non-coding and one thing sometimes eradicated in wild crops by pure choice.
It’s price stating that deleterious burden might be present in any domesticated plant selection: Potatoes, tomatoes, rice, soy and maize all have loads of further genomic parts that pure choice has not eliminated due to human breeding. Whereas it might be attainable to engineer plant genomes to have much less deleterious burdens, it’s unclear if this could have any constructive impact on the ensuing plant as these areas are sometimes inactive.
Having areas that aren’t essential to the operate of any organism might even be a bonus. If a random mutation takes place in a crucial gene, the downstream impact can be deleterious to the organism. If that very same random mutation happens in a deleterious burden gene, the end result can be much less deleterious to the organism. Round 98% of the human genome is non-coding, and whereas not all “junk DNA” is totally ineffective, it’s a snug buffer towards the really deleterious results of random mutations that alter coding genes.
Desk grapes had been additionally checked out within the research. These varieties had been discovered to have 100 instances decrease hybridization occasions, suggesting that whereas wine grapes have gone by intensive crop enchancment, the desk grape has been excellent all alongside.
Extra info:
Hua Xiao et al, Adaptive and maladaptive introgression in grapevine domestication, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2222041120
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
As anticipated, wine grapes discovered to have excessive deleterious genetic burden (2023, June 8)
retrieved 8 June 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-wine-grapes-high-deleterious-genetic.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]






