Carbene | ChemTalk
[ad_1]

Core Ideas
On this matter you’ll find out about properties of the distinction between singlet and triplet carbene, their era and properties.
Subjects Coated In Different Articles
What are Carbenes?
Carbenes are divalent (covalently bonded to 2 different atoms or teams) impartial carbon atoms with six electrons within the outermost shell, out of which two are unshared valence electrons. They’re the intermediate species fashioned by breaking teams connected to carbon atoms. The 6 electrons within the valence shell trigger electron deficiency, thus making them short-lived and extremely reactive. The only type of carbene is methylene: CH2
Normal Method= R−:C−R’ or R=C:
:CH2 (Methylene)
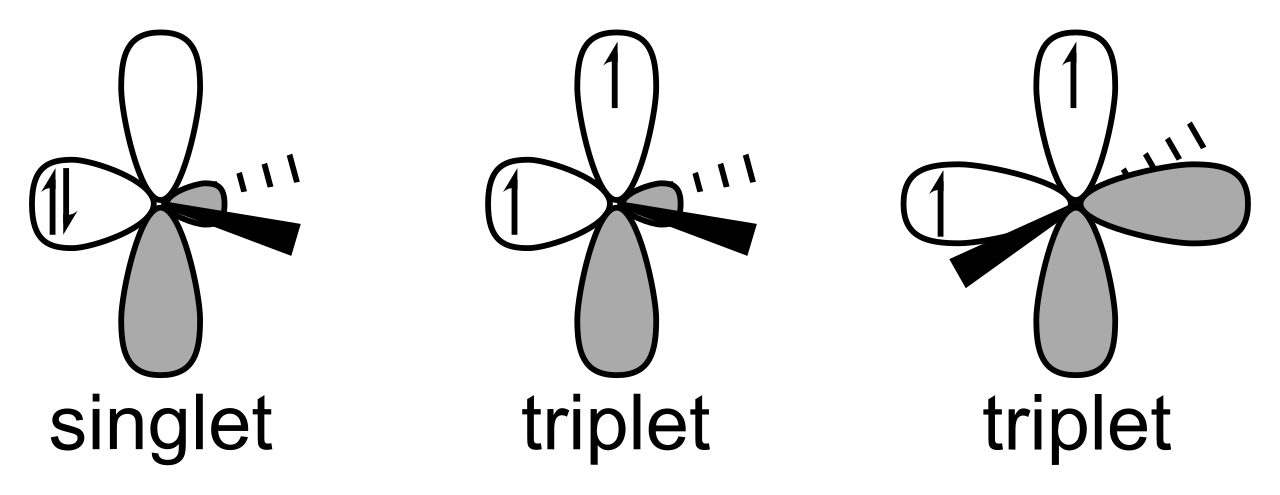
Carbenes are categorised as singlet or triplet relying on whether or not the 2 nonbonding electrons lie in the identical or totally different orbitals.
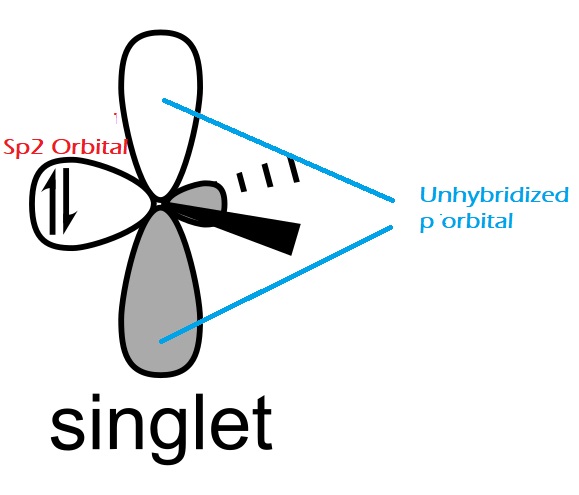
Singlet Carbene
The carbon atom in carbene is normally sp2 hybridized with three hybrid orbitals. Two of the hybrid orbitals are covalently bonded to different atoms, leaving one unhybridized p orbital and one hybridized sp2 orbital. The 2 non-bonding electrons sit paired within the hybridized sp2 orbital and have reverse spins. Thus, it’s paramagnetic.
Triplet Carbene
When the non-bonding electrons sit in two totally different orbitals (empty p-orbital and hybridized sp2 orbital) they purchase parallel spin and are often known as triplet carbene. It has linear in addition to bent geometry. The linear geometry arises when the central carbon atom types two sp hybrid orbital. On this case, two vacant p-orbitals get crammed by the non-bonding electron.

Reactivity
Typically, carbenes have an angular construction and exist of their triplet state. The triplet state is extra steady than the singlet state as a result of it has two unpaired electrons and has power 8 Kcal/mol decrease than the singlet In line with Hund’s rule of multiplicity, the multiplicity state is given by (2S+1), the place S is the variety of unpaired electrons. A triplet state having two unpaired electrons has a excessive multiplicity state which ends up in decrease power and excessive stability.
Era of Carbene
The diazo compound and hydrazones are widespread precursors for the era of carbene.
Diazo compound


Diazoalkane when handled with warmth or mild generates carbene after the removing of nitrogen.
Hydrazones

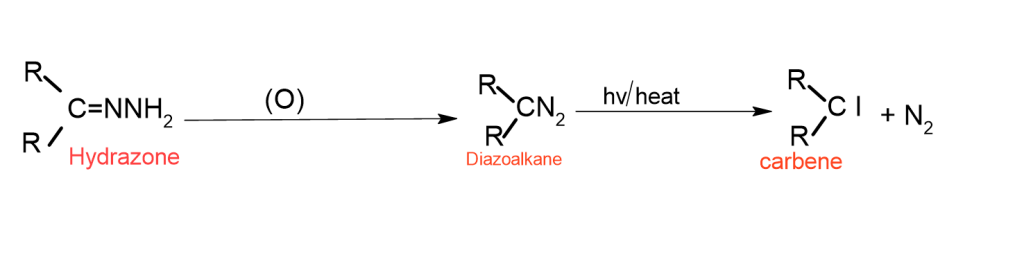
Ketone and aldehyde react with hydrazine to kind hydrazone, which oxidizes to kind a Diazo compound.
Reimer–Tiemann response
The Reimer-Tiemann response is a straightforward response the place the deprotonation of chloroform results in the formation of reactive dichlorocarbene. Right here, the carbene is an electron poor species as a result of presence of two electron-withdrawing chlorine atoms, making it web site for nucleophilic assault by the negatively modified phenoxide.

Carbenes Observe Issues
Drawback 1
What’s the function of Carbene is chemical response?
Drawback 2
What’s the distinction between singlet and triplet carbene ?
Drawback 3
Are carbenes electrophilic or nucleophilic?
Drawback 4
What are the results of substituents on Carbene?
Carbenes Observe Drawback Answer
- Carbenes are extremely reactive intermediates and help the chemical response by forming new C-C bonds and including to double bonds. Fischer carbene, a sort of divalent natural ligand is a transition steel carbene complicated.

3. Carbenes are impartial species that may be electrophilic or nucleophilic. The electrophilic nature is as a result of absence of an octet state, whereas the presence of electron- donating substituents makes them nucleophilic, for instance, Schrock carbenes.
4. If substituents connected to carbene are electron withdrawing it prefers singlet kind whereas, if the substituents are electron donating triplet kind is most popular.
[ad_2]