
Carbon Seize and Storage initiatives in Denmark in danger from bitumen formation
[ad_1]
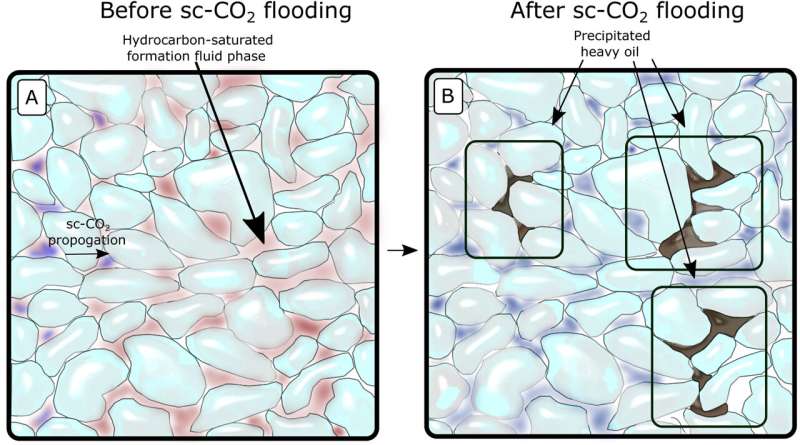
Carbon Seize and Storage (CCS) is more and more being cited to assist our international warming disaster by decreasing greenhouse fuel emissions via capturing carbon dioxide and storing deep underground. Within the Danish North Sea, chalk rocks beneath the ocean mattress maintain depleted oil and fuel reserves and at the moment are being thought of for storing carbon dioxide to capitalize upon the pre-established infrastructure from the fossil gasoline business.
Nevertheless, new analysis revealed in Marine and Petroleum Geology has thought of the potential points arising from interplay of the saved carbon dioxide with oil and fuel (hydrocarbon) residues left within the rock, which may be as much as 30% in chalk and 60% in sandstones.
Rasmus Stenshøj from Aarhus College, Denmark, and colleagues on the Vitality & Environmental Analysis Heart, U.S., carried out an experiment on a chalk pattern of some centimeters courting to the Higher Cretaceous (66 to ~100 million years in the past) from the Halfdan Subject of the North Sea.
The researchers recreated the environmental situations of the rock from the seabed earlier than injecting supercritical carbon dioxide (when it has properties of each a fuel and liquid above a sure temperature and stress) into the rock over a interval of 9 days. They then used a sequence of chemical and bodily methods to investigate the hydrocarbons current in rock samples taken earlier than and after supercritical carbon dioxide injection.
Based mostly upon temperature, completely different types of hydrocarbons are current: mild oil at 0–100°C, cellular oil at 100–200°C, semi-mobile oil at 200–300°C, motionless oil at 300–375°C and bitumen at 375–650°C.
Preliminary outcomes revealed that the supercritical carbon dioxide prompted lighter hydrocarbons to maneuver via the rock, whereas heavier varieties, reminiscent of bitumen and asphaltene-rich motionless oil, have been left behind. This will trigger blockages within the mobilization of the carbon dioxide via the rock and hamper the effectivity of the Carbon Seize and Storage system.
Importantly, the researchers discovered that the change in stress on the exit level of the system resulted in additional of the bitumen and different heavy hydrocarbon deposits, comprising as much as 10.5% of the whole rock quantity right here, whereas earlier than the experiment this was simply 4.17%. There’s general a definite development in growing heavy hydrocarbon deposition via the system as much as the exit level, thought to consequence from absorption of hydrocarbons by the supercritical carbon dioxide altering its solubility. Stenshøj and collaborators time period this growing bitumen from inlet to outlet the Avalanche Impact.
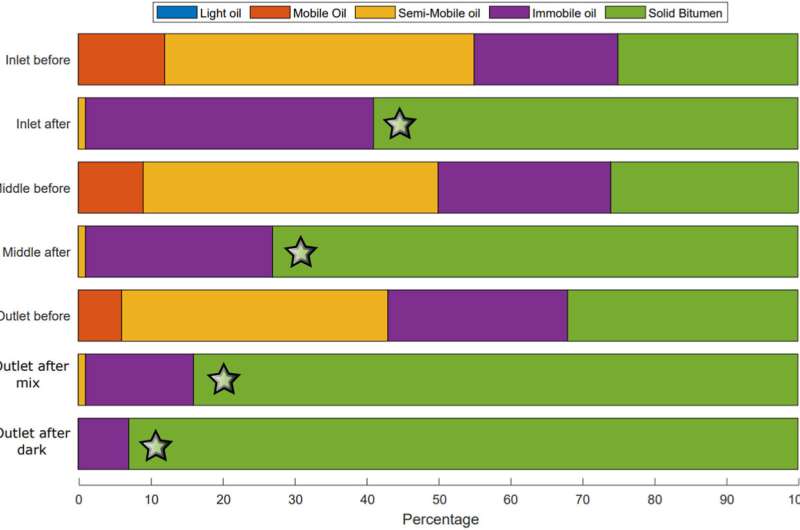
Motionless hydrocarbon and bitumen percentages across the inlet earlier than and after injection are considerably related, which the researchers state as proof of the supercritical carbon dioxide mobilizing via the crude oil part to extract lighter hydrocarbons for elimination via the system, abandoning the heavier bitumen. It’s recommended that this outcomes from a direct pushing drive of oil from the carbon dioxide, reasonably than a splitting drive.
Analyzing the samples below a microscope previous to injection revealed the pores within the rock contained a combination of water and oil, however following supercritical carbon dioxide mobilization of oil, the latter was distributed all through the rock pores changing water, and even accumulating within the microscopic shells of the traditional fossils of organisms referred to as foraminifera. This happens because the oil is drawn into the water-dominated pores by capillary forces, therefore the pattern turned extra oil saturated, which led to a change of coloration to darker brown.
The solubility of hydrocarbons in response to supercritical carbon dioxide is a fancy course of, which may be affected by modifications in temperature, stress, hydrocarbon content material and clays. Clearly the buildup of heavier hydrocarbons at exit factors can result in plugging of the Carbon Seize and Storage system, impacting its effectivity. With enhanced analysis into the siting of those storage programs primarily based upon hydrocarbon content material, the potential for making an actual distinction to international warming stays a tantalizing one.
Extra data:
Rasmus Stenshøj et al, Hydrocarbon residue in a Danish chalk reservoir and its results on CO2 injectivity, Marine and Petroleum Geology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106424
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Carbon Seize and Storage initiatives in Denmark in danger from bitumen formation (2023, August 8)
retrieved 8 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-carbon-capture-storage-denmark-bitumen.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]






