
Carbon ‘seize’ local weather tech is booming, and complicated
[ad_1]

Humanity’s failure to attract down planet-heating carbon dioxide emissions—41 billion metric tons in 2022—has thrust once-marginal choices for capping or lowering CO2 within the environment to heart stage in local weather coverage and funding.
Carbon seize and storage (CCS) and direct air seize (DAC) are each advanced industrial processes that isolate CO2 however these newly booming applied sciences are basically completely different and infrequently conflated.
Here is a primer on what they’re and the way they differ.
What’s carbon seize?
CCS siphons off CO2 from the exhaust, or flue fuel, of fossil fuel-fired energy vegetation in addition to heavy trade.
The exhaust from a coal-fired energy plant is about 12 p.c CO2, whereas in metal and cement manufacturing it’s sometimes double that.
Not like CCS, which by itself solely prevents further carbon dioxide from coming into the environment, DAC extracts CO2 molecules already there.
Crucially, this makes DAC a “adverse emissions” know-how.
It might due to this fact generate credit for corporations searching for to offset their greenhouse fuel output—however provided that the captured CO2 is completely saved underground, reminiscent of in depleted oil and fuel reservoirs or in saline aquifers.
The focus of carbon dioxide in ambient air is simply 420 components per million (about 0.04 p.c), so corralling CO2 utilizing DAC is way extra vitality intensive.
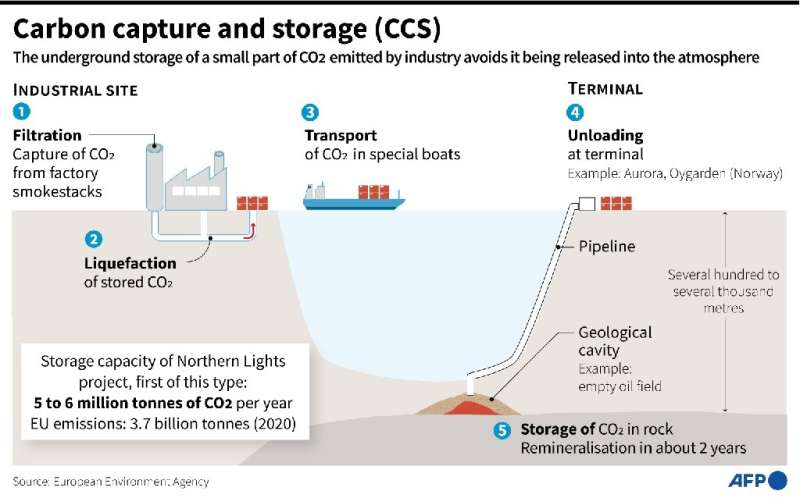
As soon as remoted utilizing both CCS or DAC, CO2 can be utilized to make merchandise reminiscent of constructing supplies or “inexperienced” aviation gasoline, although a few of that CO2 will seep again into the air.
“If the CO2 is utilized, then it isn’t removing,” stated Oliver Geden, a senior fellow on the German Institute for Worldwide Safety Affairs.
State of play
The fossil gasoline trade has been utilizing CCS because the Nineteen Seventies however to not stop CO2 from leaching into the environment.
Moderately, oil and fuel corporations inject CO2 into oil fields to extract extra crude extra shortly.
Traditionally, bolting CCS amenities onto coal- and gas-fired energy vegetation after which storing the CO2 to scale back emissions has confirmed technically possible however uneconomical.
The world’s largest CCS plant, the Petra Nova facility in Texas, was mothballed three years after opening in 2017.
However the looming local weather disaster and authorities subsidies have revived curiosity in CCS for the facility sector and past.
On the finish of 2022, there have been 35 commercial-scale amenities worldwide making use of carbon seize know-how to trade, gasoline transformation or energy technology, isolating a complete of 45 million tons (Mt) of CO2, in accordance with the Worldwide Power Company (IEA).
DAC, in contrast, may be very new.
A complete of 18 DAC vegetation globally solely captured about as a lot CO2 final yr (10,000 tons) because the world emits in 10 seconds.

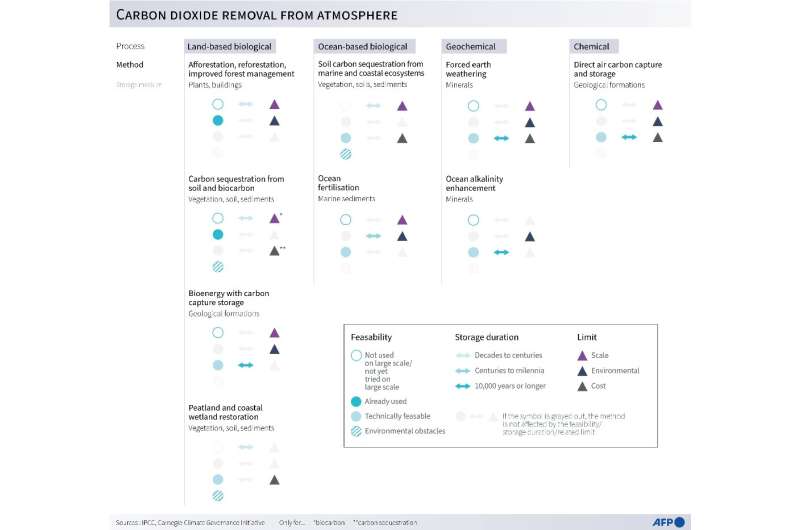
Scaling up
Each CCS and DAC should be massively scaled up if they’re to play a big function in decarbonising the worldwide economic system.
To maintain the mid-century net-zero goal in play, CCS might want to divert 1.3 billion tons a yr from energy and trade—30 occasions greater than final yr—by 2030, in accordance with the IEA.
DAC should take away 60 Mt CO2 per yr by that date, a number of thousand-fold greater than right now.
However the nascent trade is burgeoning with new actors, and the primary million-ton-per-year plant is scheduled to come back on line in the US subsequent yr, with others following.
“It is an enormous problem nevertheless it’s not unprecedented,” College of Wisconsin–Madison professor Gregory Nemet informed AFP, citing different applied sciences, together with photo voltaic panels, which have scaled up dramatically in a matter of a long time.
Making ready a web site to inventory CO2 can take as much as 10 years, so storage may change into a critical bottleneck for each CCS and DAC growth.
Price per ton
Carbon seize prices $15 to $20 per ton for industrial processes with extremely concentrated streams of CO2, and $40 to $120 per ton for extra diluted fuel streams, reminiscent of in energy technology.
DAC—nonetheless in its infancy—has a lot greater prices, ranging right now from $600 to $1,000 per ton of CO2 captured.
These prices are projected to drop sharply to $100-$300 per ton by 2050, in accordance with the inaugural State of Carbon Dioxide Removing report, revealed earlier this yr.
Observe the cash
As nations and corporations really feel the pinch from decarbonization timetables and net-zero commitments, more cash—private and non-private—is flowing towards each CCS and DAC.
In the US, the Inflation Discount Act (IRA) earmarks billions of {dollars} in tax credit for CCS.
The sooner Infrastructure Funding and Jobs Act supplies about $12 billion over 5 years.
Canada’s 2022 finances additionally extends an funding tax credit score that cuts the price of CCS initiatives in half.
South Korea and China are additionally investing closely within the sector, with China opening a 500,000 Mt plant final month in Jiangsu Province.
In Europe, assist comes on the nationwide stage and is oriented towards trade and storage, particularly within the North Sea.
For DAC, a variety of corporations—Alphabet, Shopify, Meta, Stripe, Microsoft and H&M Group—have paid right into a fund with a promise to collectively purchase a minimum of $1 billion of “everlasting carbon removing” between 2022 and 200.
Final month, JP Morgan struck a $20 million, nine-year carbon removing cope with DAC pioneer Climeworks, primarily based in Switzerland.
© 2023 AFP
Quotation:
Carbon ‘seize’ local weather tech is booming, and complicated (2023, July 4)
retrieved 4 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-carbon-capture-climate-tech-booming.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]






