
Hotter and murkier waters favor predators of guppies, examine finds
[ad_1]
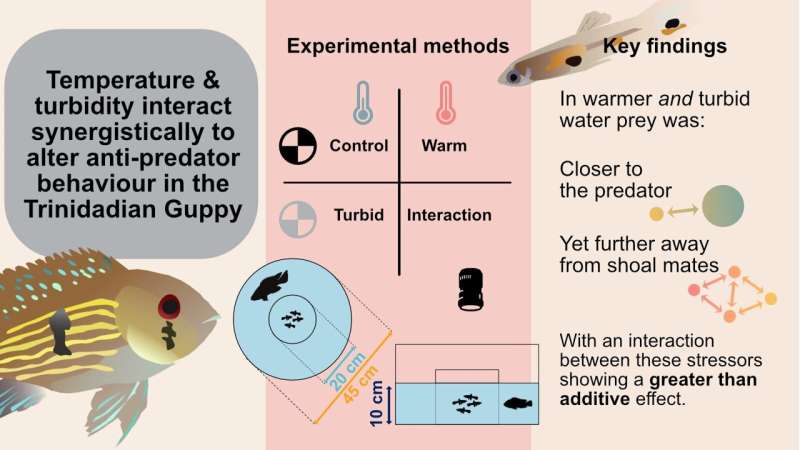
Adjustments in water situations work together to have an effect on how Trinidadian guppies defend themselves from predators, scientists on the College of Bristol have found.
Identified stressors, reminiscent of elevated temperature and decreased visibility, when mixed, trigger this fish to keep away from a predator much less, and importantly, kind looser protecting shoals.
The findings, revealed at present within the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, present guppies’ responses are extra affected by the interplay of those stressors than in the event that they acted independently.
Pure habitats are dealing with mounting environmental challenges as a consequence of human actions reminiscent of land use modifications, exploitation and local weather change.
Lead writer Costanza Zanghi from Bristol’s College of Organic Sciences, defined, “Of all of the attainable environmental parameters that may stress a system, we determined to deal with elevated temperature and water turbidity as a result of earlier analysis has proven that visible animals, like most fish, are drastically affected by them.
“We all know that hotter water impacts fish swimming capability and starvation ranges, and we additionally know that elevated turbidity, reminiscent of haziness, can change how visible predators and prey work together with each other.
“On this analysis we wished to take these frequent stressors, that are recognized to be growing in freshwater habitats globally, and see how visible fish would reply to at least one one other when they’re topic to those stressors on the similar time.
“That is essential and novel as a result of typically, particularly when a number of stressors modify related behaviors in several methods, the general final result might be very completely different from what’s proven by research the place just one stressor is examined. That is as a result of these stressors can work together in unpredictable methods.”
The group noticed the reciprocal responses between a predator and a shoal of prey underneath 4 therapies, optimum housing situations (as a management), and in therapies the place both temperature or cloudiness of water was elevated. They had been then examined with an interplay therapy the place each temperature and turbidity had been elevated on the similar time.
This took a number of weeks of trials within the lab involving 36 predators and 288 prey fish. The animals had been separated so they didn’t come to any hurt.
All of the video recordings had been then processed to acquire tremendous scale actions of all of the fish in order that the researchers may calculate the swimming speeds of all fish and the way they associated to at least one one other: how shut collectively the prey stayed and the way removed from the predator every prey tried to stay.
Co-author Milly Munro, who joined the Ioannou Group particularly for this venture mentioned, “The chance to be concerned on this examine with the group was an ideal expertise, and I’m grateful having been awarded ASAB’s Undergraduate Scholarship funding. Designing and operating the analysis alongside Costanza and the group was sensible as my first tutorial analysis expertise. I discovered lots of beneficial abilities and insights into what it takes to provide and conduct a examine of this sort, all I gained from this expertise has actually aided me in present and future initiatives.”
Zanghi mentioned, “Incorporating multi-stressors in such experiments enhances the ecological relevance and applicability of findings.
“In pure environments, organisms not often expertise remoted stressors however relatively face complicated mixtures of stressors. By investigating how organisms reply behaviorally to those real looking eventualities, the analysis turns into extra relevant to conservation and administration efforts.
“It supplies insights into how organisms could deal with and adapt to a number of stressors, aiding within the improvement of efficient methods for mitigating the unfavourable impacts of environmental change.”
Now the group plan to check whether or not the lower in anti-predator habits is as unfavourable for the prey as it might appear and never a intelligent adaptation to permit prey fish to fret much less about predators in an surroundings that retains them protected. Through the use of a wider vary of predators, they may even examine whether or not these modifications can have an effect on a number of species otherwise.
Zanghi concluded, “This examine is thrilling because it introduces essential ecological complexity within the context of predator-prey interactions.
“By incorporating extra stressors and particularly testing the potential interactions between these components, this examine considerably contributes to our understanding of the dynamics between prey and their predators in a quickly altering world.”
Extra info:
Costanza Zanghi et al, Temperature and turbidity work together synergistically to change anti-predator behaviour within the Trinidadian guppy, Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Organic Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2023.0961. royalsocietypublishing.org/doi … .1098/rspb.2023.0961
Supplied by
College of Bristol
Quotation:
Hotter and murkier waters favor predators of guppies, examine finds (2023, July 4)
retrieved 4 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-warmer-murkier-favor-predators-guppies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]






