HPLC: Excessive Efficiency Liquid Chromatography
[ad_1]

Table of Contents
ToggleCore Ideas
Excessive efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a extensively used approach in analytical chemistry to separate, establish, and quantify the person compounds in a combination of chemical compounds. It has a large scope of purposes, from prescription drugs, forensics, environmental laboratories, and extra!
Matters Lined in Different Articles
Rules of Chromatography
After a chemical response takes place, the product is usually made up of a combination of compounds: the specified product (additionally referred to as the analyte) , mixed with different aspect merchandise, impurities, and many others. (additionally referred to as the matrix). To separate the combination, chromatography can be utilized. Chromatography separates a combination primarily based on variations in polarity and makes use of two completely different components. The stationary section is a nonmoving component- in HPLC, that is usually a column filled with small silica or polymer primarily based particles. The cell section is usually some form of solvent, and it runs by way of the column, pushing out the pattern. The completely different compounds within the combination expertise completely different sights to the stationary section and the cell section on account of variations in polarity. (Nonpolar compounds appeal to nonpolar compounds, and polar compounds appeal to polar compounds!) Thus, the compounds of the combination might be pushed out (eluted) at completely different charges.
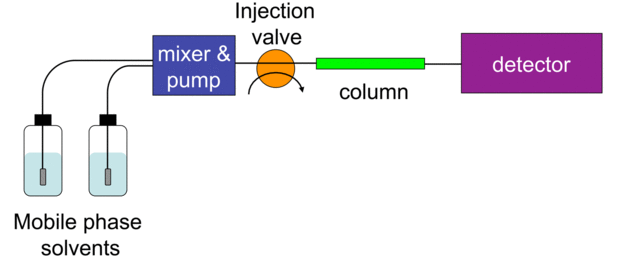
Parts of an HPLC System
- Solvent Pump: the pump pushes the solvent (cell section) by way of the system at a particularly excessive stress. Due to this excessive stress, HPLC is way quicker than different chromatography strategies corresponding to column chromatography!
- Autosampler: the autosampler ejects the pattern into the circulation of the system
- Column: the completely different chemical compounds within the pattern are separated right here, since they transfer by way of the column (stationary section) at completely different charges
- Detectors: completely different HPLC programs could use numerous detectors. Widespread detectors embrace UV-Vis, mass spectrometers, conductivity, refractive index, and many others. There are two predominant forms of detectors: particular (detect properties of the precise compound within the pattern), and bulk (detect properties primarily based on each particular compounds within the pattern and the solvents within the cell section).
- Chromatography Information System (CDS): a pc interprets the detector alerts into chromatograms that scientists can interpret
Variations of HPLC
- Regular Part Chromatography: The column (stationary section) is crammed with polar particles, generally silica. The solvent (cell section) is a comparatively nonpolar solvent. Thus, nonpolar compounds will elute first due to their increased affinity in the direction of the cell section.
- Reverse Part Chromatography: The column (stationary section) is crammed with nonpolar particles, corresponding to a C18 column (silica with a extremely nonpolar 18-carbon chain hooked up). The solvent (cell section) is a comparatively polar solvent. Since polar attracts polar, the polar compounds will elute first, reverse of regular section chromatography! That is the commonest kind of HPLC utilized in labs the world over.
- Ion Trade Chromatography: The column (stationary section) is crammed with particles with a cost reverse to that of the specified product. The pattern is handed by way of, and since reverse costs appeal to, the specified product is trapped within the column whereas byproducts wash by way of. The compound may be launched by rising the ionic power of the buffer or by altering the pH.
- Measurement Exclusion Chromatography: As an alternative of polarity, measurement exclusion chromatography separates molecules primarily based on their measurement by passing the pattern by way of a gel with numerous pores. Molecules smaller than these pores might be trapped, whereas bigger molecules might be eluted first.
Benefits and Disadvantages of HPLC
With many various chromatography strategies accessible to the everyday scientist, why is HPLC so steadily used? The primary purpose is as a result of HPLC tends to be extremely automated, which ends up in good precision and reduces the potential of human error. This results in experiments executed with HPLC being simply reproduced, one thing that’s crucial within the Scientific Technique! Moreover, the excessive stress utilized by the solvent pump, mixed with the effectivity of the machine, results in experiments being accomplished quicker. Moreover, HPLC is extraordinarily delicate. Due to this fact, it is ready to detect hint quantities of impurities and byproducts that different strategies could miss.
Nevertheless, HPLC could also be costlier than different strategies for the machines to be arrange and maintained. One other expense of working HPLC is the massive quantities of solvent the machines devour. Creating new strategies or troubleshooting errors additionally tends to be extra complicated than different strategies, requiring scientists with superior or specialised coaching. Additionally, the samples should be ready extraordinarily rigorously, for the reason that validity of an HPLC methodology relies on the accuracy and purity of the pattern, cell section, and operation of the system. Lastly, analyzing the info generated by the Chromatography Information System (CDS) could require specialised software program.
Additional Studying
[ad_2]
I am an Organizational Development Consultant, Science (Physics||Mathematics), and the Holy Qur'an teacher. To get started with me, Book Now one-to-one Session, or let us know what do you like in the contact form
Next post
Considering of Quitting Running a blog? Here is How One Blogger Turned it Round
You may also like
Aqueous Options | ChemTalk