
In Costa Rica, saving seeds to feed future generations
[ad_1]
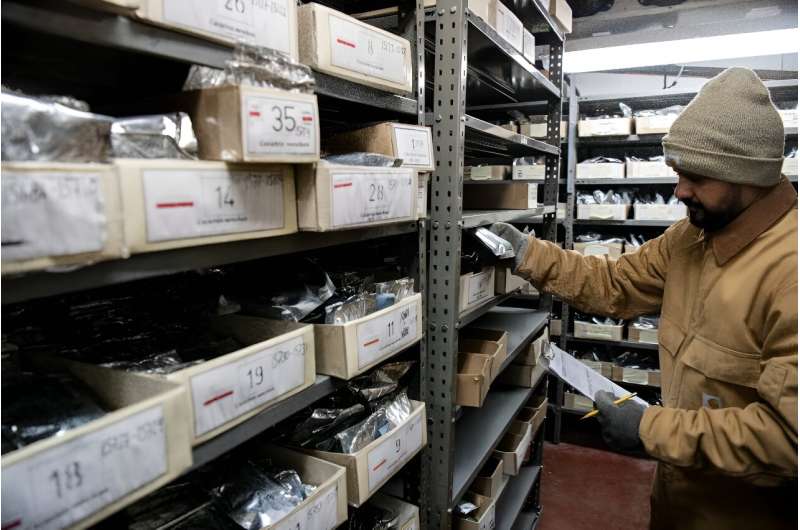

Within the tropical mountains of Costa Rica, scientists guard a treasure trove of seeds collected over many years as a bulwark in opposition to meals insecurity and local weather change.
Some 6,200 samples from 125 species of squash, chili, tomato and different edible vegetation are held on the Tropical Agricultural Analysis and Greater Schooling Middle (CATIE) close to the city of Turrialba.
In temperatures as little as minus 20 levels Celsius, the seeds may be stored for as much as 40 years for functions of analysis, genetic engineering of vegetation extra immune to pests, ailments or altering climate, or to interchange species that die out.
The financial institution “is a useful resource we now have to be used now or sooner or later,” plant geneticist William Solano advised AFP on the facility some 60 km east of the capital San Jose.
It holds seeds from 57 international locations, he stated, however about 90 % are from the Central American area, collected from markets and farms or rising wild.
The CATIE stockpile, stacked on cabinets in tons of of small, silver envelopes, contains the second-largest assortment of squash household seeds on this planet.
Most of the seeds usually are not current in banks anyplace else on this planet, in keeping with the middle.
‘Genetic archive’
“In response to local weather change, we now have right here essential supplies for meals safety which are domestically tailored” to quite a lot of local weather circumstances, starting from humidity to excessive drought, Solano advised AFP.
-
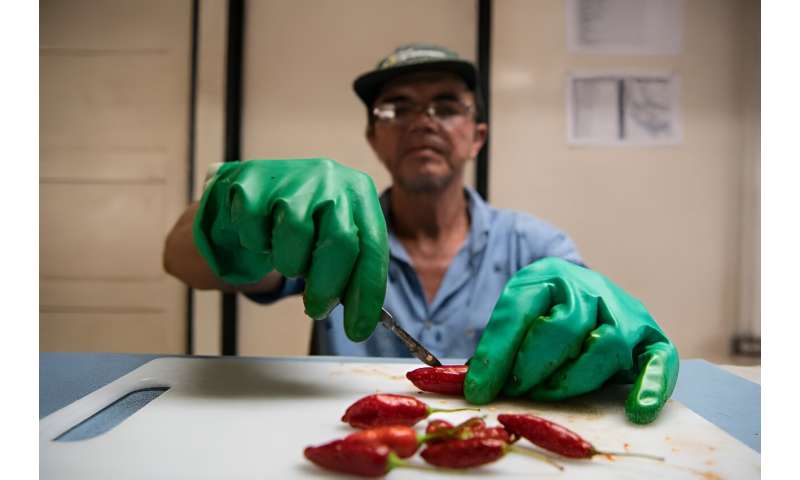

A employee removes seeds from chilies to retailer at a seed financial institution in Cartago, Costa Rica.
-
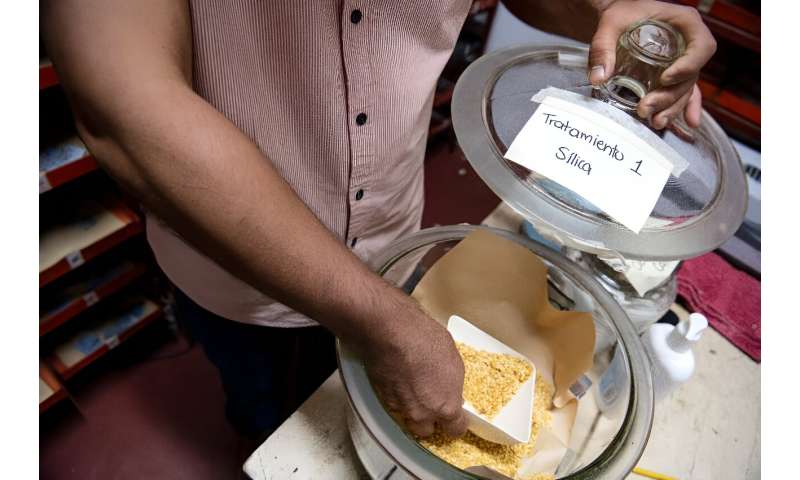
A employee organizes seeds earlier than storing them.
-
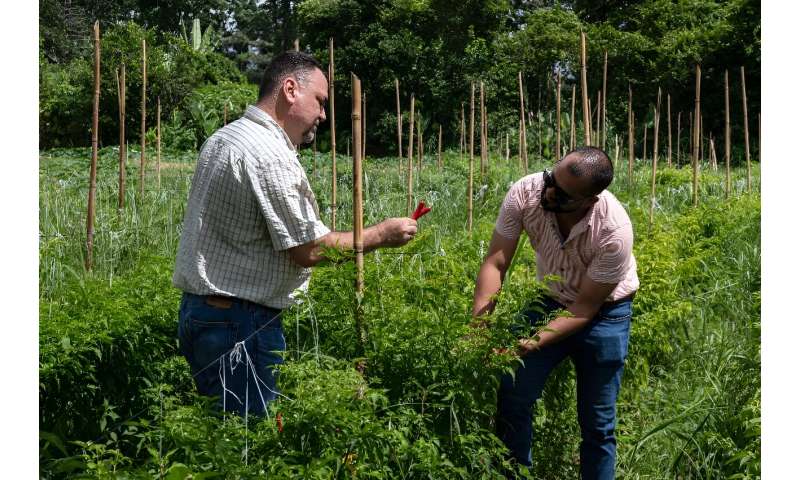

Scientists gather chili peppers to extract their seeds and retailer them.
As ever-more excessive climate threatens meals manufacturing, conventional, native seeds are important to “give sustainability to agri-food programs,” he added.
In accordance with seed knowledgeable Ester Vargas of the College of Costa Rica, “there may be variability in native seeds that offers them the flexibility to adapt to completely different circumstances” within the areas of their origin.
Seed banks just like the one at CATIE serve to ensure an availability of “crops with excessive dietary worth” for generations to return, she added.
The UN’s Meals and Agriculture Group (FAO) estimates that just about one in ten individuals on this planet suffered starvation in 2022—some 735 million in whole—with will increase in components of Africa, western Asia and the Caribbean.
The FAO says seed banks assist protect “probably the most tailored varieties” for a given area.
“As local weather change has a big influence on agricultural manufacturing, rising native varieties, which have a excessive diploma of genetic variety, is extremely essential as a result of these varieties have the flexibility to raised face up to and adapt to environmental stresses and modifications,” a doc on the group’s web site states.
CATIE agronomist Daniel Fernandez stated the financial institution additionally served one other objective: as a “genetic archive” of species that had been changed by extra modified crops and that sooner or later might have to be introduced again.
© 2023 AFP
Quotation:
In Costa Rica, saving seeds to feed future generations (2023, July 28)
retrieved 28 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-costa-rica-seeds-future-generations.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]





