New quantum magnet unleashes electronics potential » MIT Physics
[ad_1]
Researchers uncover the way to management the anomalous Corridor impact and Berry curvature to create versatile quantum magnets to be used in computer systems, robotics, and sensors.
A few of our most vital on a regular basis objects, like computer systems, medical gear, stereos, turbines, and extra, work due to magnets. We all know what occurs when computer systems turn out to be extra highly effective, however what may be doable if magnets turned extra versatile? What if one might change a bodily property that outlined their usability? What innovation may that catalyze?
It’s a query that MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Heart (PSFC) scientists Hold Chi, Yunbo Ou, Jagadeesh Moodera, and their co-authors discover in a brand new open-access Nature Communications paper, “Pressure-tunable Berry curvature in quasi-two-dimensional chromium telluride.”
Understanding the magnitude of the authors’ discovery requires a quick journey again in time: In 1879, a 23-year-old graduate pupil named Edwin Corridor found that when he put a magnet at proper angles to a strip of metallic that had a present operating by way of it, one aspect of the strip would have a larger cost than the opposite. The magnetic subject was deflecting the present’s electrons towards the sting of the metallic, a phenomenon that may be named the Corridor impact in his honor.
In Corridor’s time, the classical system of physics was the one form, and forces like gravity and magnetism acted on matter in predictable and immutable methods: Similar to dropping an apple would lead to it falling, making a “T” with a strip of electrified metallic and magnet resulted within the Corridor impact, full cease. Besides it wasn’t, actually; now we all know quantum mechanics performs a job, too.
Consider classical physics as a map of Arizona, and quantum mechanics as a automotive journey by way of the desert. The map offers a macro view and generalized details about the world, however it may well’t put together the driving force for all of the random occasions one may encounter, like an armadillo operating throughout the highway. Quantum areas, just like the journey the driving force is on, are ruled by a unique set of native site visitors guidelines. So, whereas the Corridor impact is induced by an utilized magnetic subject in a classical system, in a quantum case the Corridor impact could happen even with out the exterior subject, at which level it turns into the anomalous Corridor impact.
When cruising within the quantum realm, one is supplied with the information of the so-called “Berry section,” named after British physicist Michael Berry. It serves as a GPS logger for the automotive: It’s as if the driving force has recorded their whole journey from begin to end, and by analyzing the GPS historical past, one can higher plot the ups and downs, or “curvature” of the area. This “Berry curvature” of the quantum panorama can naturally shift electrons to at least one aspect, inducing the Corridor impact with no magnetic subject, simply because the hills and valleys dictate the trail of the automotive.
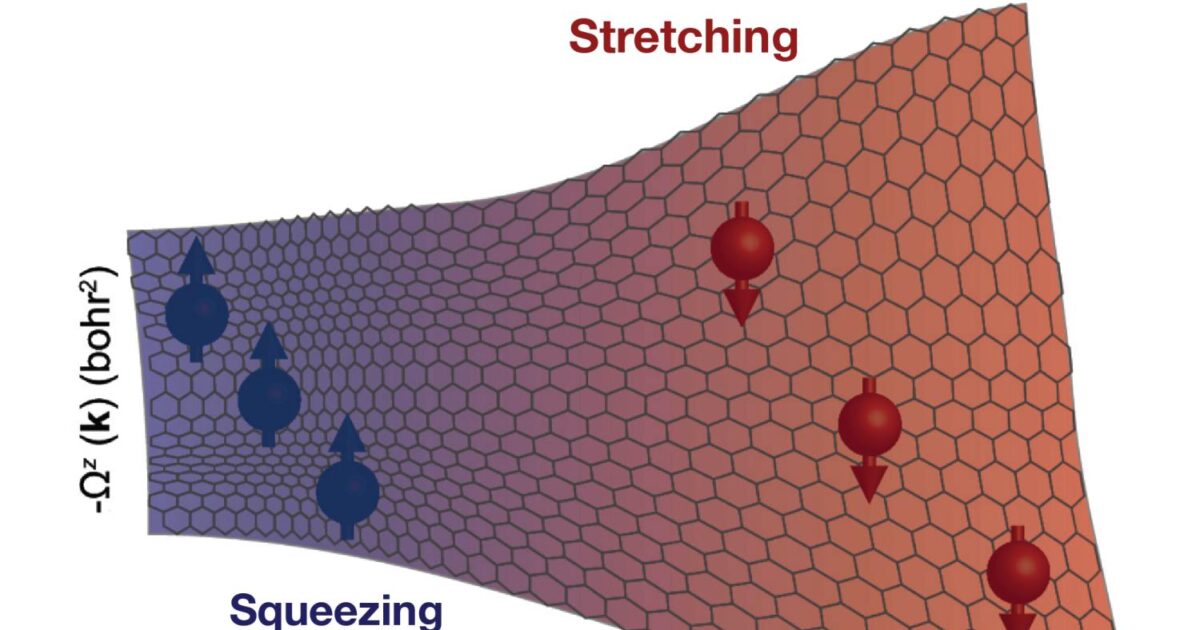
Whereas many have noticed the anomalous Corridor impact in magnetic supplies, none had been capable of manipulate it by squeezing and/or stretching — till the paper’s authors developed a technique to show the change within the anomalous Corridor impact and Berry curvature in an uncommon magnet.
First, they took half-millimeter-thick bases fabricated from both aluminum oxide or strontium titanate, each of that are crystals, and grew an extremely skinny layer of chromium telluride, a magnetic compound, on high of the bases. On their very own, these supplies wouldn’t do a lot; nevertheless, when mixed, movie’s magnetism and the interface it created with the bases onto which it was grown brought on the layers to stretch or squeeze.
To deepen their understanding of how these supplies have been working collectively, the researchers partnered with Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory (ORNL)’s Spallation Neutron Supply to carry out neutron scattering experiments — basically blasting the fabric with pictures of particles and learning what bounced again — to study extra in regards to the movie’s chemical and magnetic properties. Neutrons have been a super device for the research as a result of they’re magnetic however haven’t any electrical cost. The neutron experiments allowed the researchers to construct a profile that exposed how the chemical parts and magnetic behaviors modified at completely different ranges as they probed deeper into the fabric.
The researchers witnessed the anomalous Corridor impact and Berry curvature responding to the diploma of compacting or stretching occurring on the bottom after the movie was utilized, an commentary later verified by modeling and information simulations.
Although this breakthrough occurred on the tiniest molecular degree, the scientists’ discovery has vital, real-world ramifications. For instance, exhausting drives retailer information in tiny magnetic areas, and in the event that they have been constructed utilizing “strain-tunable” supplies just like the movie, they may retailer extra information in areas which were stretched alternative ways. In robotics, strain-tunable supplies might be used as sensors capable of present exact suggestions on robots’ actions and positioning. Such supplies can be particularly helpful for “gentle robots,” which use gentle and versatile parts that higher imitate organic organisms. Or, a magnetic machine that modified its habits when flexed or bent might be used to detect minute modifications within the atmosphere, or to make extremely delicate well being monitoring gear.
Along with Chi, Ou, and Moodera, who can also be an affiliate of the MIT Division of Physics, MIT contributors to the work embrace postdoc Alexandre C. Foucher and Professor Frances Ross of the Division of Supplies Science and Engineering.
This research was supported, partly, by the U.S. Military Analysis Workplace, U.S. Nationwide Science Basis (NSF), U.S. Workplace of Naval Analysis, U.S. Air Pressure Workplace of Scientific Analysis, and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Analysis Lab. Services entry was offered by the MIT Supplies Analysis Laboratory, MRSEC, MIT.nano, SNS and Heart for Nanophase Supplies Sciences, Division of Power Workplace of Science Person Services operated by ORNL, and Superior Cyberinfrastructure Coordination Ecosystem: Providers and Assist supported by NSF.
[ad_2]






