Gases | Intro to Gases
[ad_1]
Core Ideas
On this article, we find out about what a gasoline is, diatomic gases, the three properties of gases, gasoline legal guidelines, and gasoline section adjustments.
Matters coated in different articles
What are gases?
Gases are the highest-energy state of matter. What makes them distinctive is that they haven’t any fastened form or quantity. In contrast to solids and liquids, gases take the form of their container. They’re extremely compressible and may change quantity beneath completely different pressures and temperatures. Having an introductory understanding of gases is essential as they play a key function in numerous chemical reactions and processes.
Gases made up of 1 factor are known as monoatomic. Frequent examples are neon, argon, or helium. Nonetheless, there are some components that exist as diatomic molecules, that means that of their pure gaseous kind, these components exist as diatomic molecules with two atoms bonded collectively. A typical instance of that is oxygen! The chemical formulation of oxygen within the air we breathe isn’t ![]() , however moderately
, however moderately ![]() . Bromine, iodine, nitrogen, chlorine, hydrogen, oxygen, and fluorine are all diatomic components.
. Bromine, iodine, nitrogen, chlorine, hydrogen, oxygen, and fluorine are all diatomic components.
Properties and Legal guidelines of Gases
There are three vital properties of gases — stress, temperature, and quantity.
Stress refers back to the power exerted by gasoline molecules on the partitions of their container. It’s a results of the collisions between gasoline particles and the container’s floor. When gasoline molecules transfer quicker or there are extra gasoline molecules in a given quantity, the stress will increase. Stress is measured in models like Pascals (Pa) or atmospheres (atm).
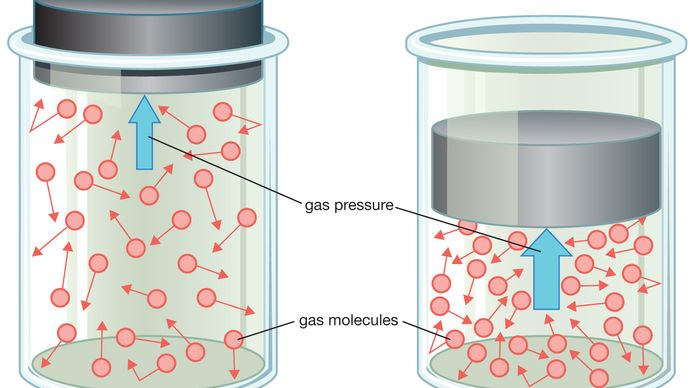
Temperature is a measure of the typical kinetic vitality of gasoline molecules. In easier phrases, it signifies how briskly the gasoline particles are transferring. When a gasoline is heated, its molecules achieve kinetic vitality, transfer extra vigorously, and its temperature rises. Conversely, cooling gasoline decreases the typical kinetic vitality of its particles and lowers the temperature. Celsius (°C), Kelvin (Ok), and Fahrenheit (°F) are mostly used to measure temperature.
Gasoline Legal guidelines
Gasoline legal guidelines are legal guidelines that describe the relationships between these completely different properties of gases.
Boyle’s Legislation states that, at fixed temperature, the amount of a given quantity of gasoline is inversely proportional to its stress. Because of this if quantity is decreased, stress will improve, and if quantity is elevated, stress will lower. Mathematically, Boyle’s legislation will be expressed as ![]() .
.
Charles’s Legislation states that, at a continuing stress, the amount of a given quantity of gasoline is immediately proportional to its temperature. Because of this if you improve the temperature of a gasoline whereas stress stays fixed, its quantity will improve, and if you lower the temperature, its quantity will lower. Charles’s legislation will be written as ![]()
Homosexual-Lussac’s Legislation states that, at a continuing quantity, the stress of a given quantity of gasoline is immediately proportional to its temperature. Because of this should you warmth up a gasoline whereas quantity stays fixed, its stress will improve, and, should you cool it down, its stress will lower. Homosexual-Lussac’s Legislation is expressed as ![]() .
.
To date, all of those legal guidelines have mentioned the relationships between two of the properties of gases whereas a 3rd property stays fixed. Nonetheless, there may be one other legislation, known as the ideally suited gasoline legislation, which includes all three of the properties of gases: stress, quantity, and temperature. The perfect gasoline legislation is a mix of Boyle’s Legislation, Charles’s Legislation, and Homosexual-Lussac’s Legislation. It may be expressed as ![]() . Be taught extra in regards to the models of the best gasoline legislation and the variations between a perfect and actual gasoline right here.
. Be taught extra in regards to the models of the best gasoline legislation and the variations between a perfect and actual gasoline right here.
Gasoline Part Adjustments
- Gasoline to strong — Deposition
- Stable to gasoline — Sublimation
- Gasoline to liquid — Condensation
- Liquid to gasoline — Vaporization
[ad_2]