
Highly effective gene enhancing method boosts rotifers in pantheon of laboratory animals
[ad_1]
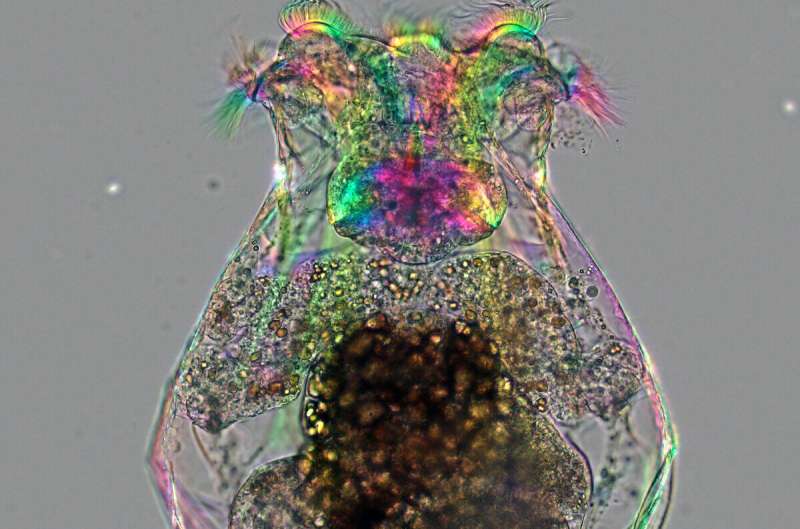
A lot about tiny, swimming rotifers makes them ultimate research topics. Though barely seen to the bare eye, these clear animals and their innards are readily considered beneath a microscope. What’s extra, they develop readily in laboratory tradition, providing scientists an in any other case difficult-to-obtain perspective from their nook of the animal kingdom.
Nonetheless, whereas rotifers have been used experimentally for greater than a century by many analysis teams, scientists have up to now lacked the power to readily manipulate rotifers’ genetics, inserting a tough restrict on the experiments they will run with these animals.
A joint effort by Kristin Gribble and David Mark Welch on the Marine Organic Laboratory (MBL) has overcome this problem by devising a way for exactly altering the rotifers’ genomes utilizing the gene enhancing system CRISPR-Cas9. In experiments described in PLOS Biology, their workforce edited two genes and added a genetic sequence to provide modifications that the rotifers handed down by means of generations.
“Our methodology seems to be a really sensible strategy to generate a lot of genetically altered rotifers pretty rapidly,” mentioned Mark Welch, a senior scientist at MBL and director of the Josephine Bay Paul Middle for Comparative Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Not solely will this advance profit his lab and Gribble’s, which use rotifers to check the biology of growing old, DNA restore mechanisms, and different elementary questions, it is going to “open the sphere to permit extra individuals to work with these animals,” Mark Welch mentioned.
Creating a microscopic, water-dwelling lab animal
Sure residing issues—the bacterium E. coli, fruit flies, and mice, for instance—have change into nicely established as mannequin organisms that scientists routinely use in analysis. Taken collectively, nonetheless, they do not adequately characterize the total variety of life.
The MBL workforce goals so as to add rotifers to this group of genetically tractable organisms as a result of, as tiny invertebrates with shut ties to the ancestors of contemporary animals, they provide an vital perspective on evolution, improvement, and different elements of biology.

To develop rotifers as mannequin organisms, researchers want the capability to tweak these animals’ genomes. In 2017, MBL Interim Director Melina Hale of College of Chicago offered Gribble and Mark Welch with funding to plot a way for doing so utilizing CRISPR-Cas9. The purpose of cultivating a better number of mannequin organisms later grew to become formalized as MBL’s New Analysis Organisms initiative.
Now extensively employed in analysis, CRISPR-Cas9 makes exact cuts inside DNA, which researchers use to close down or alter genes. First, nonetheless, they need to get the CRISPR system into the animals.
Tremendous-sawdust-sized specks darting about in water, rotifers make for unusually difficult targets. After many unsuccessful makes an attempt to carry them nonetheless, first writer Haiyang Feng, then a postdoctoral scientist at MBL, devised an answer: By immersing them in a high-viscosity answer and administering a low stage of an anesthetic, he slowed the animals sufficient to seize them one after the other with mild suction by means of a hole needle.
With the animal, all the time a feminine, in place, he injected the gene enhancing system into the a part of its physique that provides vitamins to the eggs. The offspring that hatched from these eggs then carried the mutations, which they handed on to their offspring.
On this manner, the workforce inactivated vasa, a gene essential to animal improvement, inflicting the rotifers to cease reproducing after just a few generations. By turning off a second gene, mlh3, they prevented the rotifers from producing male offspring. And, lastly, by including a piece of genetic code containing “cease” directions into mlh3, they achieved the identical impact.
New prospects for rotifer analysis
Each researchers intend to make use of the CRISPR-based methodology to genetically alter rotifers for their very own analysis. As a part of her work exploring how moms’ age can have an effect on the traits of their offspring, Gribble, an affiliate scientist at MBL, is investigating the function of mitochondria, the energy-producing element of cells. The brand new method will permit her to tag or alter mitochondria. Mark Welch, in the meantime, plans to make use of it to discover the molecular mechanisms behind one rotifer species’ means to revive after fully drying out, together with how they restore injury to their DNA.
Research like these are solely the start. “This new instrument, together with the convenience of elevating rotifers within the lab, will make it doable to make use of them to reply a lot of questions we aren’t even fascinated about but,” Gribble says.
Extra data:
Haiyang Feng et al, Extremely environment friendly CRISPR-mediated gene enhancing in a rotifer, PLOS Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001888
Offered by
Marine Organic Laboratory
Quotation:
Highly effective gene enhancing method boosts rotifers in pantheon of laboratory animals (2023, August 4)
retrieved 4 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-powerful-gene-approach-boosts-rotifers.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]






