What’s an alloy? | ChemTalk
[ad_1]
Idea Introduction – Alloys
An alloy is a mix of two or extra metals. Many alloys exist that mix completely different metals and completely different ratios of steel. On this tutorial, study what an alloy is, the properties of alloys, and a few of the commonest alloys used at present.
Matters Coated in Different Articles
What’s an Alloy?
An alloy is a mix of two elemental supplies to make a metallic substance. The primary part is a steel (usually a couple of steel) and metallic properties are retained within the new combination. An alloy will be both a compound (strong) or answer (liquid). Mostly alloys exist as a strong at room temperature.

Properties of Alloys
There are numerous helpful and tunable properties of alloys together with hardness, corrosion resistance, and ductility.
Ductility is the flexibility for a fabric to deform domestically. Glass just isn’t ductile and subsequently breaks when strain is utilized. Nevertheless, alloys can bend barely to native strain with out breaking, that means they’re extra ductile. This is a vital property in constructing supplies. Alloys are inclined to have greater ductility.
Corrosion resistance can also be an necessary property of supplies that will likely be uncovered to the climate or harsh circumstances. Corrosion happens when a substance undergoes a chemical response equivalent to oxidation, and slowly wears away the fabric. Rust is a standard product of corrosion. Alloys generally have greater corrosion resistance than elemental metals.
Hardness measures how simply a fabric is scratched. The Mohs hardness scale measures this property. Pure metals are a lot softer and extra malleable to work with in lots of manufacturing eventualities. In building, a really malleable materials doesn’t present structural integrity nicely.
How is an alloy made?
Alloys are mostly made by heating the required materials till they’re molten. Then the parts combine collectively. The molten substance flows right into a mould. The mould is allowed to chill, creating the brand new materials within the desired form.
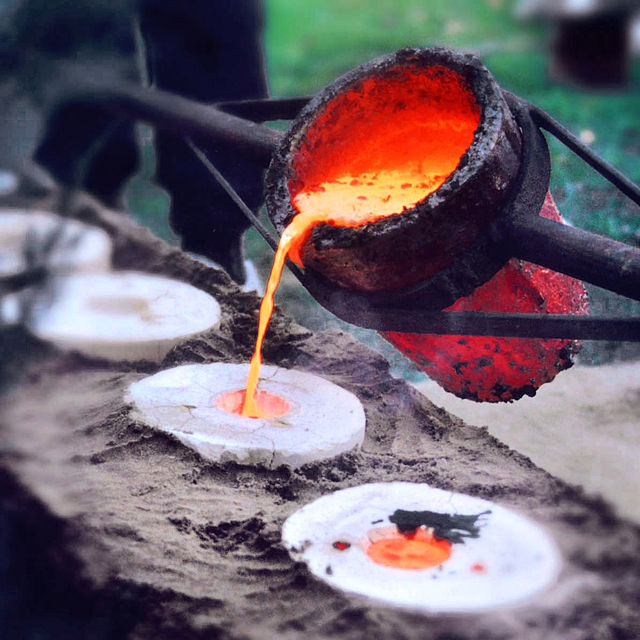

It can be crucial that the supplies be soluble with one another. There are some metals, equivalent to iron and copper, that don’t combine collectively. Due to this fact these mixtures make unhealthy supplies as an alloy.
Impurities in Alloys
An alloy is by definition an unpure substance. Nevertheless, when referring to impurities in an alloy it references a component that ought to not presupposed to be there. For instance, metal generally accommodates the impurity sulfur (which is meant to simply be carbon and iron). The commonest impurity depends on the principle steel within the alloy. In aluminum alloys, lithium, calcium, and sodium are the commonest impurities. Oxygen causes vast unfold impurities because of the formation of oxides with metals.
The issue with impurities is that the change the properties of an alloy. For instance, the fabric could also be weaker, and extra liable to interrupt, the place impurities are current. Many steps throughout manufacturing happen to keep away from impurities.
Frequent Alloys
- Brass: Brass is a mixture of copper and zinc.
- Bronze: Copper and tin are the 2 parts in bronze. The Bronze Age (3,000-1,200 B.C.) is known as after this alloy as a result of the invention of the fabric modified that interval of historical past so dramatically.
- Solid Iron: Forged iron is a fabric generally utilized in cooking pans. The fabric accommodates very excessive percentages of iron (>90%) and a small proportion of carbon.
- Metal: Metal accommodates carbon (a nonmetal) and iron. Metal has improved energy and fracture resistance in comparison with pure iron.
- Sterling Silver: A standard part of jewelery is sterling silver. The usual for this alloy is 92.5% silver and seven.5% copper.
- Solder: Lead and tin combination. Used for connecting wires.
- Fusible Alloy: A category of alloys which have low melting factors. Soldering supplies and hearth sprinklers generally use this materials. They’re nice in hearth sprinklers as a result of they hearth heats the alloy to the purpose that melts it. The melting alloy breaks a seal that enables water to launch to quench the hearth. These supplies soften round 100oC.

Additional Studying
[ad_2]